WellData Implementation Guide - Local Development build (v0.1.2) built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) Build Tools. See the Directory of published versions
Anonymous Login
Goals and assumption
A pilot has been defined by Verslavingskunde Nederland (VKN) that wants to prove the integration of e-health modules with Health Tools Interoperability (HTI) and the use of Self Sovereign Identities (SSI) with a an Anonymous ID published by GIDS Open Standaarden. The case of HTI will not be discussed in this document. This document describes the application of Anonymous ID published by GIDS Open Standaarden, which allows anonymous logins. Whereas most self sovereign attributes are related to things like driver's licenses and social security numbers. Contemporary e-Health applications make use of relatable identifiers such as email or social security number. Public available self-help platforms have a) no need to identify the user with a relatable identifier, b) users highly prefer anonymity when participating in publicly available platforms, c) anonymous use of the software platforms makes the platform less vulnerable to leaking sensitive user data. This project makes use of an assigned identifier that is unrelated to the user, other than that the possession of the identifier can be used to identify a recurring user as the same as before.
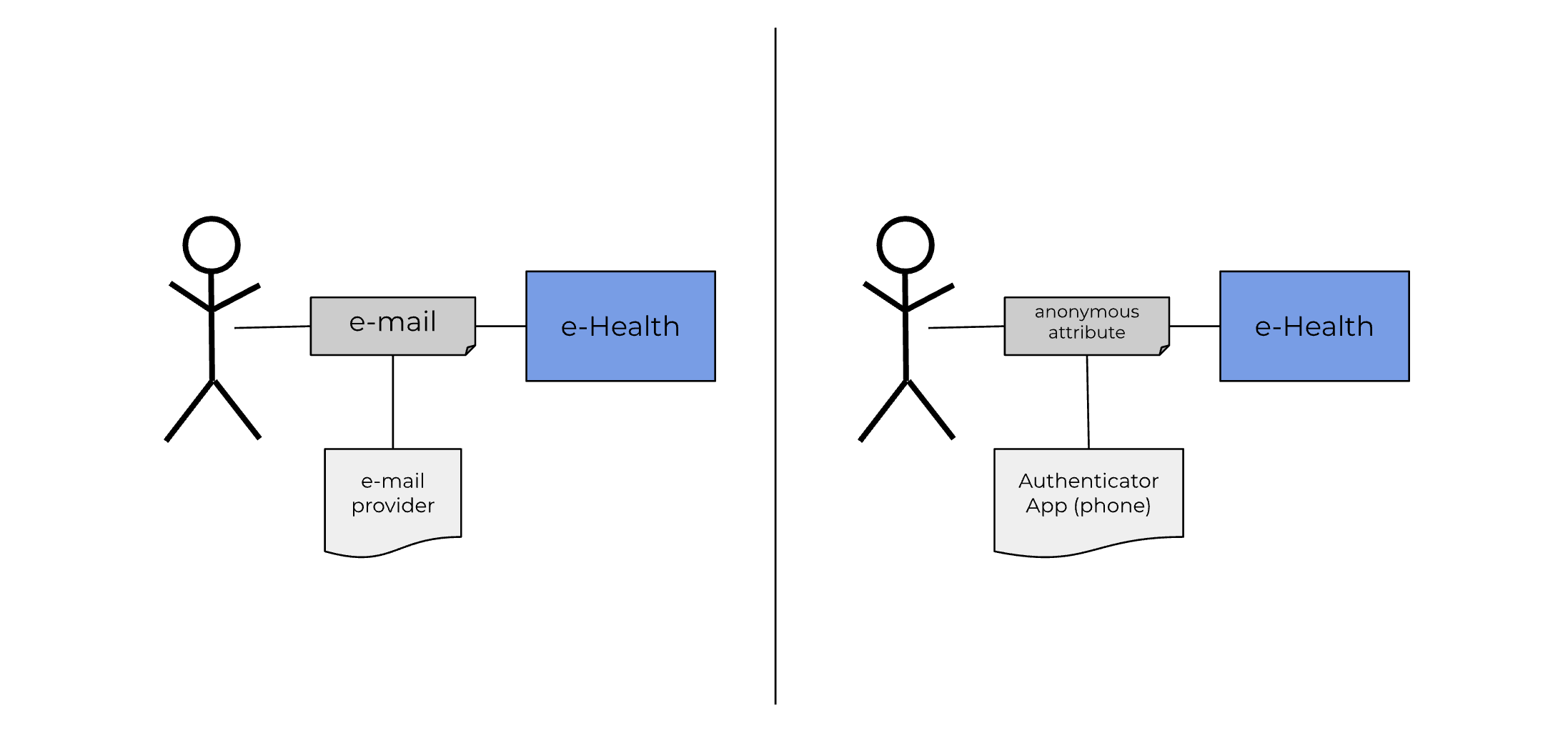
The main advantage of such an approach is that the launch of e-Health applications becomes truly anonymous, there is no way the e-Health supplier can learn the real identity of the user. In case of data breaches or unauthorized access the e-Health supplier does not run the risk of leaking personal information.
Architectural overview
The link with the GIDS anon VC requires secrets and a complicated integration with both the GIDS platform as a service. Furthermore, there is a generic part of user interaction that is shared between all platforms that can be centralized. For implementers convenience, the MS Auth middleware has been developed. Keep in mind that the MS Authenticator uses open standards for reading attributes; implementers can choose to make use of the MS Authenticator without the middleware. The middleware takes care of the task of common user interaction and integration with MS Authenticator, and exposes a simple OAut2 interface to the applications and platforms.
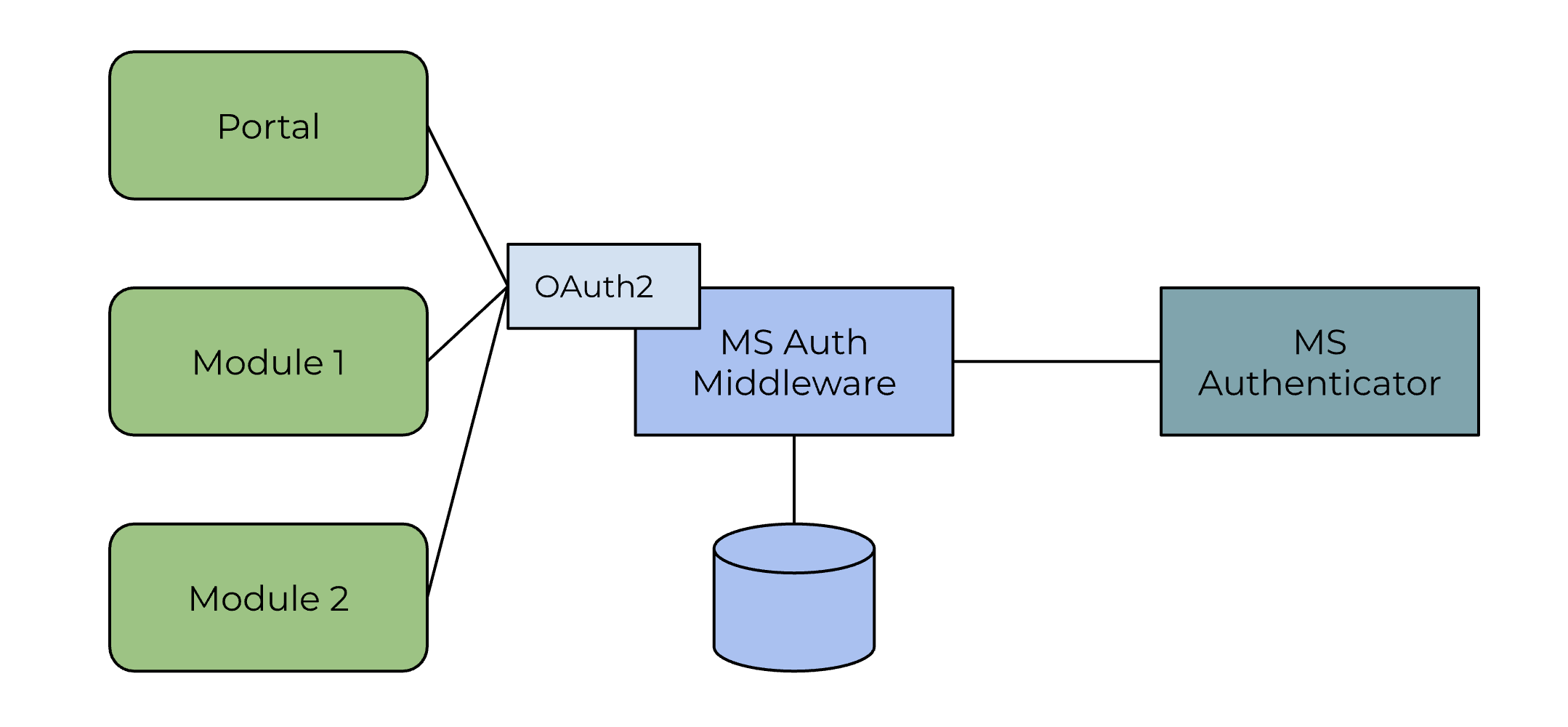
From the portal and module perspective, the middleware is integrated with an OAuth2 Authorization Code Flow.
Functional perspective
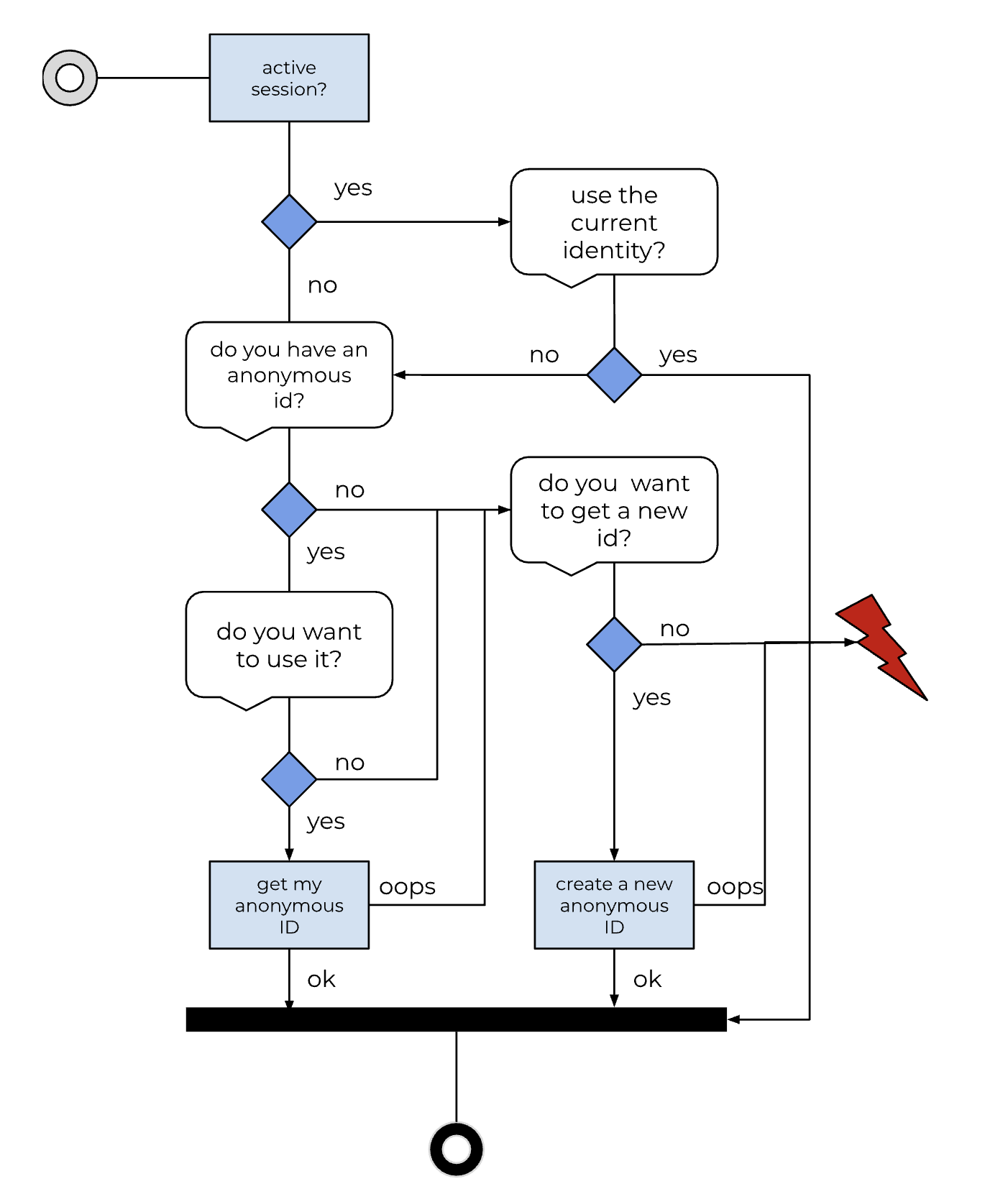
The diagram below explains the user interaction of the middleware. This interaction is performed each time the user interacts with the middleware. This interaction is performed by the middleware and from a portal or module perspective it should be considered as provided by the middleware.